Insurance is an essential safety net, protecting individuals and businesses from unforeseen financial burdens. However, the cost of insurance can be a significant expense, often leaving consumers wondering how premiums are calculated and what factors influence their price. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of insurance costs, exploring the underlying principles, key components, and strategies for managing your premiums.
From understanding the role of risk assessment and coverage levels to navigating the impact of demographic factors and lifestyle choices, this guide provides a clear and insightful overview of the factors that shape insurance costs. We’ll examine the historical trends and potential future directions of insurance pricing, equipping you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your insurance needs.
Understanding Insurance Costs
Insurance premiums, the monthly or annual payments you make for coverage, are determined by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions about your insurance needs and minimizing your overall costs.
Factors Influencing Insurance Premiums
Insurance premiums are not arbitrary; they are calculated based on a thorough assessment of risk. Here are some key factors that insurers consider:
- Type of Coverage: Different types of insurance, such as health, auto, or home insurance, carry varying levels of risk. For example, health insurance premiums are influenced by factors like age, health history, and location, while auto insurance premiums are affected by driving record, vehicle type, and location.
- Risk Assessment: Insurers use sophisticated algorithms and data analysis to assess the likelihood of a claim. Factors like age, driving record, credit score, and even location can influence your risk profile.
- Coverage Amount: The higher the coverage amount you choose, the higher your premium will be. This is because insurers are assuming greater financial responsibility in the event of a claim.
- Deductible: Your deductible is the amount you pay out of pocket before your insurance coverage kicks in. A higher deductible typically translates to lower premiums, as you are taking on more financial risk.
- Claims History: Your past claims history plays a significant role in determining your premium. A history of frequent claims can lead to higher premiums, as insurers perceive you as a higher risk.
- Location: Factors like crime rates, natural disaster risk, and traffic density can impact your insurance premiums. For example, homeowners in areas prone to hurricanes or earthquakes may face higher premiums.
- Competition: The level of competition in the insurance market can influence premium pricing. In areas with more insurers, you may have more options and potentially lower premiums.
Risk Assessment and Insurance Costs
Risk assessment is the cornerstone of insurance pricing. Insurers use a variety of methods to evaluate the likelihood of a claim, including:
- Statistical Analysis: Insurers leverage historical data on claims frequency and severity to develop statistical models that predict risk.
- Data Mining: Modern insurers use data mining techniques to analyze vast amounts of data, including demographics, driving records, and even social media activity, to identify patterns and assess risk.
- Underwriting: Underwriters review applications and conduct interviews to assess the risk associated with individual policyholders. They consider factors like health history, driving record, and financial stability.
“The principle of insurance is to share the risk of loss among a large number of people, so that no one individual bears the full burden.”
Variations in Insurance Costs
The cost of insurance can vary significantly depending on the type of coverage:
- Health Insurance: Premiums for health insurance are influenced by factors like age, health status, location, and coverage level. Individuals with pre-existing conditions or who live in areas with higher healthcare costs may face higher premiums.
- Auto Insurance: Auto insurance premiums are determined by factors such as driving record, vehicle type, location, and coverage level. Drivers with a history of accidents or traffic violations, or those who drive high-performance vehicles, may face higher premiums.
- Home Insurance: Home insurance premiums are influenced by factors like location, property value, age of the home, and coverage level. Homes in areas prone to natural disasters or with high crime rates may have higher premiums.
Key Components of Insurance Costs

Insurance premiums are the payments made to an insurance company in exchange for coverage against potential risks. These premiums are calculated based on several factors, including the type of coverage, the amount of coverage, the insured’s risk profile, and administrative costs.
Coverage Levels
The amount of coverage you choose directly impacts your premium. Higher coverage levels, such as comprehensive or collision coverage for car insurance, offer greater protection but come with a higher price tag.
- Basic Coverage: This level provides minimal coverage, typically covering only legal liability for accidents. It is often the most affordable option but offers limited protection. For example, a basic car insurance policy might only cover damages you cause to another person’s property in an accident.
- Comprehensive Coverage: This level expands on basic coverage by including protection against non-collision events, such as theft, vandalism, or natural disasters. While offering greater protection, it comes with a higher premium. For example, comprehensive coverage for your car would cover damage to your vehicle caused by a hail storm, even if you were not involved in an accident.
- Collision Coverage: This level covers damages to your vehicle resulting from an accident, regardless of fault. This coverage is typically more expensive than basic coverage but provides greater financial security in the event of an accident. For example, collision coverage would cover repairs to your car if you hit a parked vehicle.
Deductibles
Deductibles are the out-of-pocket expenses you agree to pay before your insurance coverage kicks in. Higher deductibles usually result in lower premiums, as the insurer assumes less risk.
- Low Deductible: A low deductible means you pay a smaller amount out-of-pocket before your insurance covers the rest. However, this usually comes with a higher premium. For example, a low deductible of $250 for your car insurance means you would pay $250 for repairs after an accident, and your insurance would cover the remaining costs.
- High Deductible: A high deductible means you pay a larger amount out-of-pocket before your insurance covers the rest. This usually results in a lower premium. For example, a high deductible of $1,000 for your car insurance means you would pay $1,000 for repairs after an accident, and your insurance would cover the remaining costs.
Co-pays
Co-pays are fixed amounts you pay for specific medical services, such as doctor visits or prescription drugs. Co-pays are typically lower than deductibles and are designed to encourage responsible healthcare utilization.
Table of Cost Variations
The following table illustrates the cost variations in premiums based on different coverage levels and deductibles:
| Coverage Level | Deductible | Premium |
|—|—|—|
| Basic | $500 | $50 |
| Basic | $1,000 | $40 |
| Comprehensive | $500 | $100 |
| Comprehensive | $1,000 | $80 |
| Collision | $500 | $150 |
| Collision | $1,000 | $120 |
Note: These are hypothetical examples and actual premiums will vary based on factors such as age, driving history, location, and other risk factors.
Real-World Examples
- Car Insurance: A young driver with a clean driving record might choose a basic coverage plan with a high deductible to save on premiums. However, if they are involved in an accident, they will have to pay a significant amount out-of-pocket before their insurance covers the rest.
- Health Insurance: A healthy individual might opt for a high-deductible health plan to lower their monthly premiums. However, if they require expensive medical treatment, they will have to pay a substantial amount out-of-pocket before their insurance kicks in.
Factors Affecting Individual Premiums
Insurance premiums are not a one-size-fits-all proposition. They are carefully calculated based on a variety of factors that assess the individual’s risk profile. Understanding these factors can help you make informed decisions about your insurance needs and potentially save money.
Demographic Factors
Demographic factors play a significant role in determining insurance premiums. These factors are often used to assess an individual’s risk of needing to file a claim.
- Age: Younger individuals generally pay lower premiums for certain types of insurance, such as auto insurance, because they are statistically less likely to be involved in accidents. However, as people age, premiums tend to increase due to factors like health risks and driving experience. For health insurance, older individuals generally pay higher premiums due to the increased likelihood of health issues.
- Location: The location where you live can significantly influence your insurance premiums. Insurance companies consider factors such as crime rates, traffic congestion, and weather patterns to assess the likelihood of claims. For example, individuals living in urban areas with high traffic density may pay higher auto insurance premiums compared to those in rural areas.
- Driving History: A clean driving record is a major factor in determining auto insurance premiums. Individuals with a history of accidents, traffic violations, or DUI convictions are considered higher risk and will likely pay higher premiums.
- Credit Score: While this may seem counterintuitive, credit scores are increasingly used by insurance companies to assess risk. Individuals with lower credit scores are often associated with a higher risk of making claims, leading to higher premiums.
Risk Profiles
Insurance companies carefully assess risk profiles to determine individual premiums. This assessment considers factors that influence the likelihood of an insurance claim.
- Good Driving Record: Individuals with a clean driving history, free of accidents or violations, are considered lower risk and often enjoy lower auto insurance premiums.
- Poor Driving Record: Individuals with a history of accidents, traffic violations, or DUI convictions are considered higher risk and will likely pay higher premiums. Insurance companies may also impose surcharges for specific offenses, such as speeding tickets or driving without insurance.
Lifestyle Choices
Lifestyle choices can significantly impact insurance premiums, particularly for health and life insurance.
- Smoking: Smokers are generally considered higher risk for health insurance and life insurance. This is because smoking increases the likelihood of developing various health issues, leading to higher premiums.
- Health Habits: Individuals with healthy habits, such as regular exercise, a balanced diet, and maintaining a healthy weight, are often considered lower risk for health insurance. This can translate to lower premiums.
Insurance Cost Trends
Insurance costs have been on the rise for decades, driven by a complex interplay of economic, societal, and technological factors. Understanding these trends is crucial for individuals and businesses alike, as it informs financial planning and risk management strategies.
Historical Trends in Insurance Costs
Analyzing historical trends in insurance costs reveals distinct patterns across various categories.
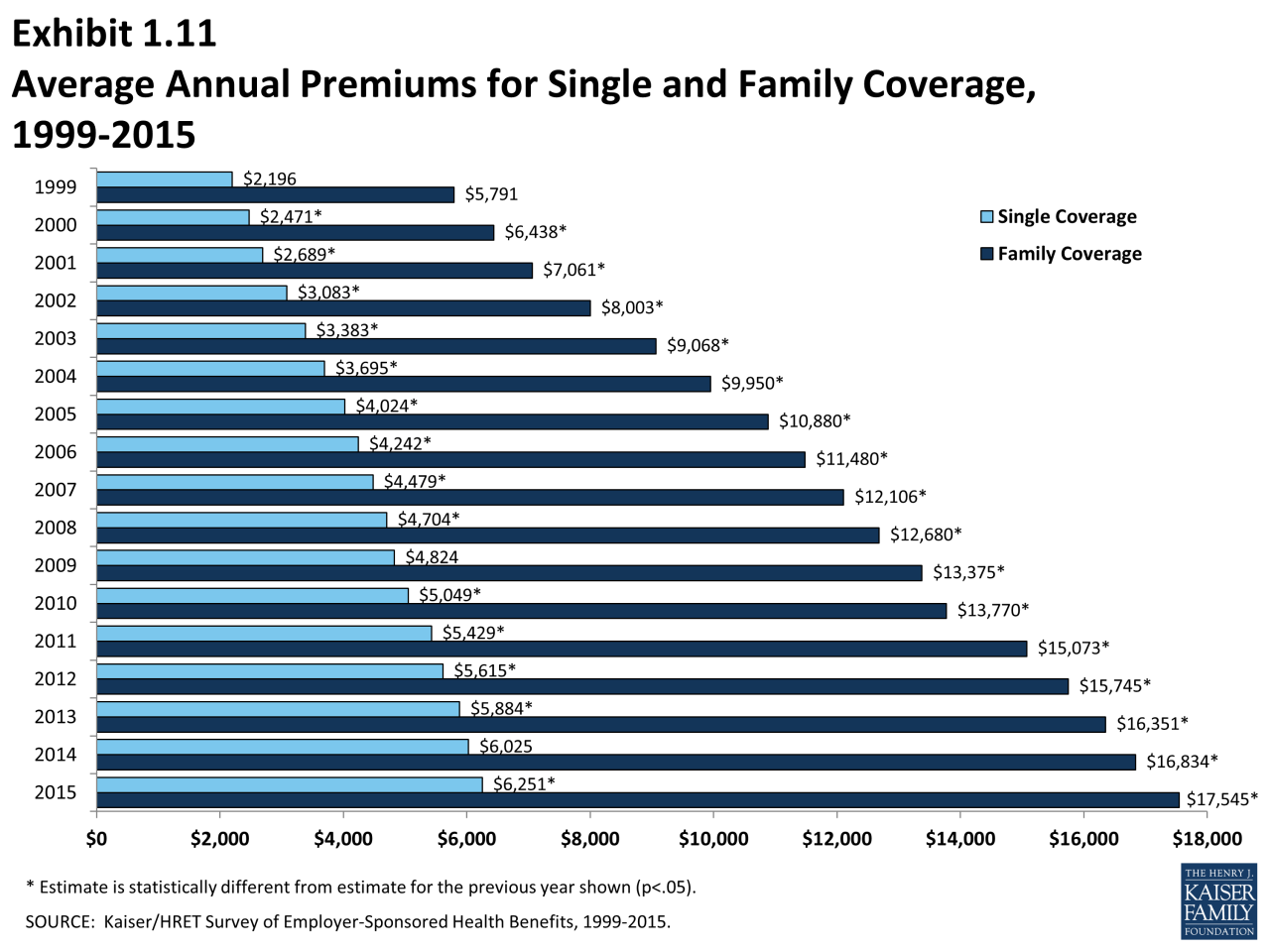
- Health Insurance: Health insurance premiums have consistently increased over the past few decades, largely driven by rising healthcare costs. The average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance has more than doubled since 1999, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
- Auto Insurance: Auto insurance premiums have also trended upwards, influenced by factors such as rising vehicle repair costs, increased traffic congestion, and more frequent claims due to distracted driving.
- Homeowners Insurance: Homeowners insurance premiums have been affected by factors like rising construction costs, more severe weather events, and increased property values.
Economic and Societal Factors Driving Insurance Cost Trends
A number of economic and societal factors contribute to the upward trend in insurance costs.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, leading to higher costs for everything, including insurance premiums.
- Healthcare Costs: Rising healthcare costs are a major driver of health insurance premium increases. Factors contributing to these costs include technological advancements, an aging population, and increased utilization of healthcare services.
- Increased Litigation: The rise in lawsuits and insurance claims has led to higher insurance premiums, as insurers must cover legal costs and settlements.
- Natural Disasters: More frequent and severe natural disasters, such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and wildfires, have increased the cost of property insurance.
Potential Future Trends in Insurance Costs
Predicting future insurance cost trends is challenging, but several factors suggest continued upward pressure.
- Continued Inflation: Inflation is expected to remain elevated in the near term, which will likely continue to push insurance premiums higher.
- Technological Advancements: Technological advancements in healthcare and other industries can lead to both higher and lower insurance costs. For example, while new treatments and technologies can improve health outcomes, they can also be expensive.
- Climate Change: Climate change is expected to exacerbate natural disasters, leading to higher property insurance premiums.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Cybersecurity threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, which could lead to higher insurance premiums for businesses and individuals.
Strategies for Reducing Insurance Costs
In today’s economy, every dollar counts. Understanding how to reduce insurance costs can significantly impact your budget, leaving more money for other financial goals. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can employ to lower your premiums, from simple lifestyle changes to proactive shopping around.
Improving Driving Habits
Safe driving habits not only protect you and others on the road but also directly impact your insurance premiums. Insurance companies reward safe drivers with lower rates, recognizing their reduced risk of accidents.
- Defensive Driving Courses: Enrolling in a defensive driving course can demonstrate your commitment to safe driving practices. Many insurers offer discounts for completing these courses.
- Avoid Distracted Driving: Distracted driving, including texting, talking on the phone, or eating, significantly increases the risk of accidents. By eliminating these distractions, you reduce your risk and potentially lower your insurance premiums.
- Maintain a Clean Driving Record: A clean driving record is crucial for lower insurance rates. Avoid speeding tickets, reckless driving violations, and accidents.
Bundling Policies
Bundling your insurance policies with the same provider can offer substantial savings. Insurance companies often provide discounts for combining multiple policies, such as auto, home, renters, or life insurance.
Bundling multiple policies with the same insurer can lead to significant discounts on your premiums.
Comparing Quotes from Different Insurance Providers
Shopping around for insurance quotes is crucial to finding the best rates. Insurance companies have varying pricing structures, and what’s affordable for one might be exorbitant for another. Online comparison tools and insurance brokers can help you quickly gather quotes from multiple providers.
- Online Comparison Tools: Websites like Policygenius, Insurify, and NerdWallet allow you to compare quotes from various insurance companies simultaneously. This saves you time and effort.
- Insurance Brokers: Brokers work on your behalf to find the best insurance policies and rates from multiple providers. They can navigate the complex world of insurance and provide expert advice.
Discounts and Incentives
Insurance companies often offer discounts and incentives to attract and retain customers. These discounts can vary depending on the insurer, your policy, and your personal circumstances.
- Good Student Discounts: Students with good grades often qualify for discounts on their auto insurance premiums. This reflects the lower risk associated with responsible students.
- Safe Driver Discounts: Drivers with a clean driving record and no accidents or violations are eligible for safe driver discounts.
- Loyalty Discounts: Insurers often reward long-term customers with loyalty discounts for staying with them.
- Home Security Discounts: Installing security systems, such as alarms and cameras, can lower your home insurance premiums by reducing the risk of theft or damage.
Insurance Cost Comparison
Comparing insurance costs across different providers is crucial for finding the best value for your needs. Understanding the factors that influence these costs and how they vary across different insurance types can help you make informed decisions.
Average Costs of Different Insurance Types
To understand the cost variations across different insurance types, it’s helpful to look at average premiums. The following table provides a snapshot of average costs for various insurance types across major insurance providers in the United States:
| Insurance Type | Average Annual Premium |
|—|—|
| Auto Insurance | $1,500 |
| Homeowners Insurance | $1,200 |
| Health Insurance | $6,000 |
| Life Insurance | $1,000 |
| Renters Insurance | $200 |
Note: These are just average figures and actual premiums can vary significantly based on individual factors such as age, location, coverage, and driving history.
Cost Variations Across Insurance Companies
Insurance companies utilize different pricing models and risk assessments, resulting in varying premiums for similar coverage. A visual representation of this cost variation can be depicted using a bar chart.
[Image: A bar chart showing average annual premiums for auto insurance across five major insurance companies, with the bars representing each company’s premium and the x-axis showing the name of each insurance company.]
The chart illustrates the cost variations across different insurance companies for auto insurance. As you can see, there can be significant differences in premiums, even for similar coverage levels.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Insurance Provider Based on Cost
When choosing an insurance provider, it’s important to consider several factors beyond just the initial premium cost. Here are some key factors to evaluate:
- Coverage: Ensure that the coverage offered aligns with your specific needs and protects you against potential risks.
- Deductibles and Co-pays: Understand the deductibles and co-pays associated with the policy, as these can significantly impact your out-of-pocket expenses in case of a claim.
- Customer Service: Research the company’s reputation for customer service and claims processing. Look for companies with positive reviews and a history of resolving claims efficiently.
- Financial Stability: Consider the financial stability of the insurance company. A financially sound company is more likely to be able to pay claims in the future.
- Discounts: Inquire about available discounts, such as safe driving discounts, multi-policy discounts, and good student discounts, which can potentially lower your premium.
By carefully evaluating these factors and comparing quotes from multiple insurance providers, you can find the most cost-effective and comprehensive insurance coverage for your needs.
The Impact of Insurance Costs on Individuals and Businesses
Insurance costs represent a significant financial outlay for both individuals and businesses. The burden of these costs can be substantial, influencing financial planning, decision-making, and overall economic well-being. Rising insurance costs, driven by factors like inflation, increased claims, and regulatory changes, can have a ripple effect across various sectors, impacting individuals’ budgets, businesses’ profitability, and even broader economic trends.
The Financial Burden of Insurance Costs on Individuals and Families
The cost of insurance can significantly impact an individual’s or family’s budget, particularly for essential coverage like health, auto, and homeowners insurance. Rising premiums can lead to financial strain, especially for those with limited income.
- Health Insurance: The increasing cost of healthcare, coupled with rising insurance premiums, can lead to a substantial portion of an individual’s income being allocated to health insurance. This can leave less disposable income for other necessities, such as food, housing, and education. For instance, in the United States, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored health insurance for a family of four was $22,221 in 2022, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation. This represents a significant financial burden for many families.
- Auto Insurance: The rising cost of vehicle repairs and medical expenses associated with accidents has driven up auto insurance premiums. This can be particularly challenging for individuals with limited financial resources, as they may be forced to choose between paying for insurance and other essential expenses. In some cases, individuals may opt for lower coverage limits to reduce premiums, leaving them vulnerable in the event of a serious accident.
- Homeowners Insurance: The increasing frequency and severity of natural disasters, coupled with rising construction costs, have contributed to higher homeowners insurance premiums. This can impact the affordability of homeownership, especially for those on a fixed income or living in areas prone to natural disasters.
The Implications of Rising Insurance Costs on Businesses and Their Profitability
Insurance costs are a major expense for businesses, impacting profitability and competitiveness. Rising premiums can erode profit margins, forcing businesses to adjust pricing, cut costs, or even reduce investments in growth and innovation.
- Increased Operating Costs: Businesses face rising costs for various types of insurance, including liability, property, workers’ compensation, and product liability. These increased costs can directly impact profitability, particularly for businesses with thin profit margins.
- Reduced Investment: Rising insurance costs can lead businesses to reduce investments in areas such as research and development, expansion, and employee training. This can hinder long-term growth and competitiveness.
- Price Increases: To offset rising insurance costs, businesses may be forced to increase prices for their goods or services. This can impact consumer demand and competitiveness, particularly in price-sensitive markets.
Insurance Cost Decisions for Individuals and Businesses
The financial burden of insurance costs can influence decision-making for both individuals and businesses.
- Individuals: Individuals may choose to reduce their insurance coverage or even forgo coverage altogether to save money. This can leave them financially vulnerable in the event of a major loss. For example, individuals may choose to opt for a higher deductible on their auto insurance to lower their premiums, but this can lead to significant out-of-pocket expenses in the event of an accident.
- Businesses: Businesses may explore strategies to reduce insurance costs, such as increasing safety measures, implementing risk management programs, and negotiating with insurers. However, these strategies can require significant investments and may not always be feasible for all businesses. For example, businesses may invest in workplace safety training to reduce the risk of accidents and potentially lower their workers’ compensation insurance premiums.
Government Regulations and Insurance Costs
Government regulations play a significant role in shaping the insurance landscape, influencing both the costs and availability of insurance products. These regulations aim to protect consumers, ensure market stability, and promote fair competition.
Impact of Specific Regulations on Insurance Premiums
Regulations can directly impact insurance premiums by imposing specific requirements on insurers, such as mandated coverage, pricing restrictions, and solvency standards.
For example, healthcare reform legislation in the United States has had a significant impact on health insurance premiums. The Affordable Care Act (ACA) mandates that insurers cover essential health benefits, prohibits insurers from denying coverage based on pre-existing conditions, and requires insurers to offer plans with specific benefit packages. These regulations have led to increased costs for insurers, which are often passed on to consumers in the form of higher premiums.
- Mandated Coverage: Regulations requiring insurers to cover specific risks, such as essential health benefits under the ACA, can increase costs by expanding the pool of insured individuals and the range of covered services.
- Pricing Restrictions: Regulations that limit insurers’ ability to price policies based on factors such as age, health status, or geographic location can also affect premiums. For example, the ACA prohibits insurers from charging higher premiums to individuals with pre-existing conditions.
- Solvency Standards: Regulations requiring insurers to maintain adequate capital reserves to ensure their financial stability can also impact premiums. These regulations aim to protect consumers by ensuring that insurers can meet their obligations even in the event of unexpected losses.
The Future of Insurance Costs
The insurance industry is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer behavior, and societal shifts. These factors will inevitably shape the future of insurance costs, leading to both opportunities and challenges for insurers and policyholders alike.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
The rapid pace of technological innovation is poised to significantly influence insurance costs in the years to come. The adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics will transform how insurers assess risk, price policies, and manage claims.
- AI-powered risk assessment models can analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns and predict future events, leading to more accurate and personalized pricing.
- IoT devices, such as smart home sensors and wearable fitness trackers, can provide real-time data on policyholder behavior, allowing insurers to offer discounts for safer driving habits or healthier lifestyles.
- Data analytics can help insurers identify emerging risks and trends, enabling them to proactively adjust pricing and coverage to better reflect changing conditions.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics in Insurance Pricing
AI and data analytics are revolutionizing insurance pricing by enabling insurers to develop more sophisticated and personalized models. These technologies can analyze a wide range of factors, including demographic data, driving records, credit scores, and even social media activity, to create a more comprehensive picture of individual risk.
“AI-powered pricing models can identify subtle correlations and patterns in data that would be difficult or impossible for humans to detect, leading to more accurate and equitable pricing.” – [Source: Harvard Business Review]
This level of granularity allows insurers to offer more tailored policies and discounts to low-risk individuals, while also increasing premiums for those who pose a higher risk. This shift towards personalized pricing can lead to both cost savings for responsible policyholders and increased costs for those with higher risk profiles.
The Influence of Consumer Behavior and Societal Changes
Consumer behavior and societal trends are also playing a crucial role in shaping the future of insurance costs. The growing adoption of ride-sharing services, the rise of telemedicine, and the increasing prevalence of natural disasters are all influencing insurance pricing and coverage.
- Ride-sharing services are changing the way people travel, leading to a decrease in car ownership and potentially impacting auto insurance premiums.
- Telemedicine is making healthcare more accessible and affordable, which could potentially lead to lower health insurance costs.
- The frequency and severity of natural disasters are increasing, leading to higher premiums for homeowners and businesses in vulnerable areas.
These trends highlight the importance of insurers adapting their pricing models and coverage options to meet the evolving needs of their customers. As consumer behavior and societal shifts continue to shape the insurance landscape, insurers must remain agile and innovative to remain competitive.
Insurance Cost Transparency and Consumer Protection
Insurance costs are a significant expense for individuals and businesses alike, making transparency in pricing and policy terms crucial for informed decision-making. Consumer protection regulations play a vital role in safeguarding individuals from unfair insurance practices, ensuring a level playing field and promoting fair competition within the market.
The Importance of Transparency in Insurance Pricing and Policy Terms
Transparency in insurance pricing and policy terms empowers consumers to make informed decisions. Consumers can compare different insurance products and choose the most suitable option for their needs when they understand the factors that influence pricing and the terms and conditions of coverage. This transparency fosters trust and confidence in the insurance industry, as consumers feel assured that they are not being taken advantage of.
The Role of Consumer Protection Regulations in Safeguarding Individuals from Unfair Insurance Practices
Consumer protection regulations are essential in safeguarding individuals from unfair insurance practices. These regulations establish standards for insurance companies, including requirements for clear and concise policy language, disclosure of pricing factors, and protection against discriminatory practices. They also provide avenues for consumers to file complaints and seek redress if they feel they have been treated unfairly.
Examples of How Individuals Can Advocate for Greater Transparency and Protection in the Insurance Market
Individuals can actively participate in advocating for greater transparency and protection in the insurance market by:
- Engaging with Regulators: Individuals can contact their state insurance commissioner or other relevant regulatory bodies to express concerns about transparency and unfair practices. These agencies often have public comment periods or forums where individuals can voice their opinions.
- Supporting Consumer Advocacy Groups: Consumer advocacy groups play a crucial role in advocating for consumer rights and protection in the insurance market. Individuals can support these groups by donating, volunteering, or participating in their campaigns.
- Sharing Experiences and Information: Sharing personal experiences with insurance companies, both positive and negative, can help raise awareness about transparency and consumer protection issues. This can be done through online forums, social media, or by contacting consumer protection agencies.
- Demanding Transparency from Insurers: Consumers can actively ask insurance companies for clear explanations of their pricing and policy terms. They can also request clarification on any unclear or ambiguous language in their insurance policies.
Insurance Cost as a Social Issue
The escalating cost of insurance is not merely an economic concern; it has profound social implications, particularly for vulnerable populations. High insurance premiums can create a barrier to accessing essential services, exacerbating existing inequalities and impacting overall well-being.
Impact on Access to Healthcare
The cost of health insurance is a significant barrier to healthcare access, especially for low-income individuals and families. High premiums can force individuals to choose between paying for essential needs and obtaining necessary medical care. This can lead to delayed or forgone care, resulting in poorer health outcomes and increased healthcare costs in the long run.
The Kaiser Family Foundation reported that in 2022, the average annual premium for employer-sponsored family health insurance was $22,221, representing a significant financial burden for many households.
Impact on Access to Housing and Other Essential Services
Rising insurance costs also affect access to housing and other essential services. Homeowners insurance premiums have been increasing in recent years, making it more challenging for individuals to afford homeownership. Additionally, increased insurance costs for renters can lead to higher rents, further straining household budgets.
The National Association of Insurance Commissioners reported that the average annual premium for homeowners insurance increased by 10% between 2021 and 2022, highlighting the growing burden on homeowners.
Initiatives to Address Insurance Affordability
Several initiatives are being implemented to address the affordability of insurance. These include:
- Government subsidies: Government programs like the Affordable Care Act provide subsidies to help low- and middle-income individuals afford health insurance.
- Community health centers: These centers provide affordable healthcare services to underserved communities.
- Consumer education programs: Programs that educate consumers about insurance options and help them find affordable plans can empower them to make informed decisions.
Epilogue
Navigating the complexities of insurance costs requires a nuanced understanding of the factors that influence premiums. By understanding the key components, identifying your individual risk profile, and exploring strategies for cost reduction, you can take control of your insurance expenses and ensure you’re adequately protected while maximizing value. As technology continues to reshape the insurance landscape, staying informed about emerging trends and consumer protection measures is crucial for making smart choices about your insurance coverage.

